Rapidly Renewable Fibers
We’re on a mission to end deforestation by applying extraordinary technology to everyday products.
We need trees to reduce carbon, clean the air, and protect the environment – not to make toilet paper.
Typically, it takes 30 years for a pine tree to grow to maturity for processing while wheat, corn stalks, sugar cane and other plants take weeks. We work with US farmers to source these ingredients, reducing local pollution, methane gas, and creating new revenue.
We typically use the following rapidly renewable resources to create our solutions:
Corn, Sugar, Wheat, Bamboo
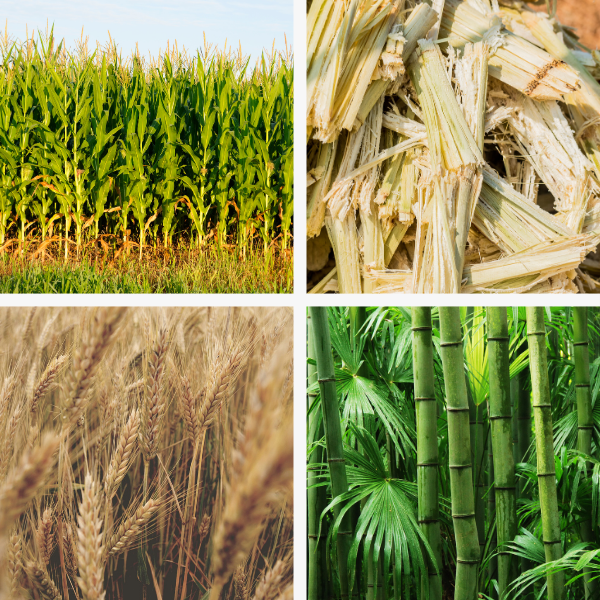
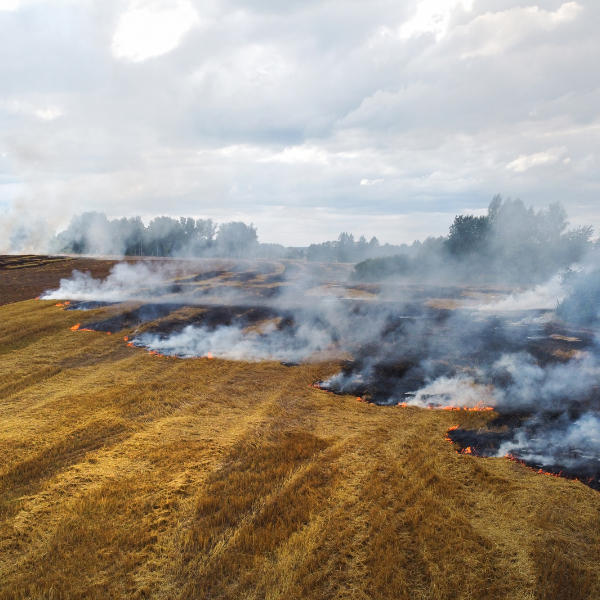


Only 30-40% of these plants are used for harvesting. The byproducts (up to 70% of these plants) are burned (carbon pollution), piled or sent to a landfill (methane gassing). Reusing these byproducts is important for reducing environmental pollution, increasing resource utilization, and working towards a net zero solution.
The Benefits of Rapidly Renewable Fibers
Rapidly renewable fibers offer several environmental benefits.
-
- Firstly, their short growth cycle means they can be harvested more frequently, reducing the pressure on land and resources. This makes them an excellent alternative to slow-growing crops like trees used for paper production.
-
- Secondly, these fibers are often biodegradable or compostable, meaning they can break down naturally over time, minimizing waste and reducing landfill usage.
-
- Another significant advantage of rapidly renewable fibers is their lower carbon footprint. As they require less energy and resources to produce, their overall environmental impact is significantly lower compared to traditional fibers or synthetic materials.
Single-use disposables in the food service industry, such as plates, bowls, and cutlery, have traditionally been made from plastic or paper. However, rapidly renewable fibers offer a more sustainable alternative.
For instance, bamboo fiber-based cups, plates and bowls are not only eco-friendly but also sturdy and heat-resistant. They provide an excellent solution for restaurants and catering services looking to reduce their environmental impact without compromising on functionality.
The packaging industry is one of the largest contributors to single-use waste. However, rapidly renewable fibers offer sustainable alternatives for packaging materials such as bags, boxes, and wrappers.
The use of rapidly renewable fibers in single-use disposables is still in its early stages but shows immense potential for growth.
Innovations such as fiber blending techniques and surface treatments are being explored to enhance the functionality of rapidly renewable fibers in various applications.
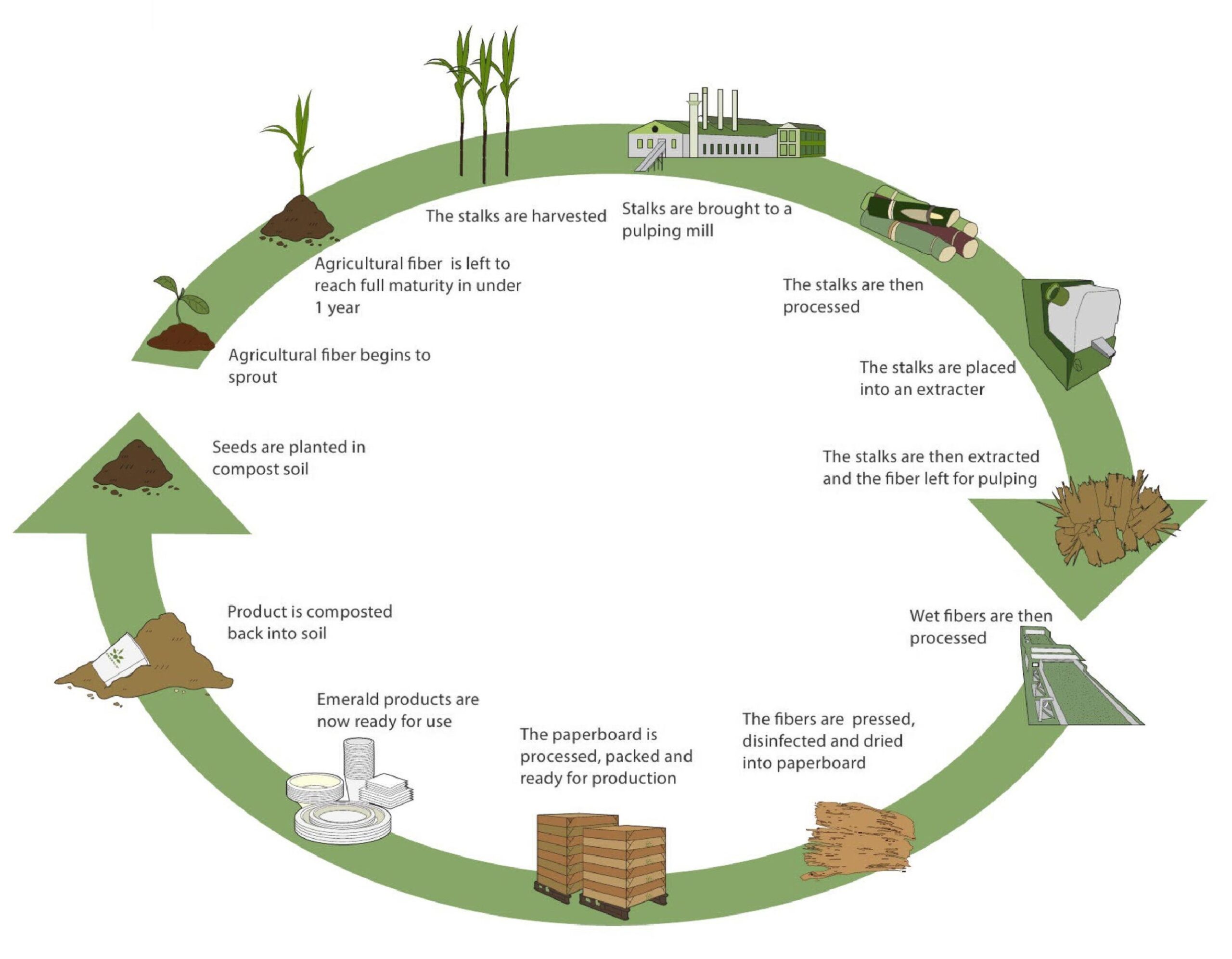
Plant to Paper
We are constantly innovating to source new fibers and create new ways to bypass the use of trees, plastic, and other environmentally destructive materials. Our Plant to Paper products are making it easier to make responsible choices.
Bamboo
Bamboo is considered one of the top choices for paper production due to several reasons. Firstly, bamboo is a highly sustainable resource that can be cultivated on a large scale. It requires less time and fewer resources to grow bamboo plantations compared to other materials.
Trees take decades to regenerate after being harvested, but bamboo is known for its rapid growth rate – making it one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth. Some bamboo species can grow over a meter per day.
Bamboo can be grown in any season and in an environmentally stressed area. To lessen the impact on the environment, bamboo paper can be easily recycled like paper made from any other resource.
Corn
Crop stalk refers to the stems and leaves of mature crops, such as wheat, rice, corn, potato, canola, cotton, and sugar cane. After harvesting the seeds, the remaining stalks are rich in nutrients and organic matter. As the by-product of crops, the main treatment is incineration. Once regarded as the main cause of air pollution, this incineration is detrimental to the environment and a waste of resources.
A new environmentally-friendly pulping technology has been developed, which utilizes agricultural waste as raw materials. This innovative method involves the use of specific microorganisms as inoculants, along with engineering treatment and biological fermentation processes, to decompose and oxidize components such as lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose.
Sugar
Bagasse is a residue that is obtained from crushing sugarcane stalks during the sugar production process. It is a dry and pulpy material that has various uses, including the manufacturing of paper, pulp, building materials, and as a biofuel for energy, heat, and electricity production.
Sugarcane is an incredibly fast-growing and renewable resource. Being a by-product of sugar production, bagasse is a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional paper production, which relies on wood and consumes more energy.
Wheat
Wheat is the principal food grain produced in the US. In 2023/24, U.S. farmers are estimated to produce a total of 1.81 billion bushels of winter, spring, and durum wheat. After harvesting wheat grains, the remaining stalks and leaves are typically seen as waste. If these leftovers are burned or left in the field, they can contribute to pollution and environmental harm.
The process of making wheat straw pulp involves converting leftover wheat straw into pulp, which is used to create paper, making it a sustainable solution.
